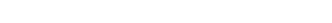ARC-SAT and Satellite Projects
Advanced Research Center for Space Science and Technology (ARC-SAT)
The Advanced Research Center for Space Science and Technology (ARC-SAT) at Kanazawa University’s Institute of Science and Engineering was established in July 2019. The center focuses on advancing space-related knowledge through research involving satellites and space probes while fostering the development of future technologies and talent. Key activities include:
- Satellite Development: Collaborating on domestic and international satellite projects and developing Kanazawa University’s unique microsatellites.
- Innovative Observation Technologies: Developing world-class observation technologies to achieve groundbreaking scientific discoveries.
- Deepening Space Understanding: Exploring phenomena related to the Sun, Earth, and deep space to enhance our understanding of the cosmic environment.
- Talent Development: Training individuals with project management skills, broad perspectives, and teamwork abilities through hands-on satellite development projects.
ARC-SAT strives to unravel the mysteries of space while contributing to the development of next-generation leaders in the field of space science.
Kanazawa University Satellite Projects
ARC-SAT leads the Kanazawa University Satellite Project, bringing together researchers in space science and engineering. This project combines hands-on education in space science and engineering with a commitment to achieving cutting-edge scientific results through microsatellite development.
①Kanazawa University’s First Satellite: “KOYOH”
Launched on December 2, 2023, KOYOH is Kanazawa University’s first microsatellite. Developed through the collaboration of faculty and students in science and engineering, KOYOH is a 50-kg-class satellite designed to observe X-rays and gamma rays. Its mission aims to shed light on phenomena such as black hole formation and celestial bodies emitting gravitational waves. The satellite was also selected as a demonstration theme for JAXA’s Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration Program No. 3.
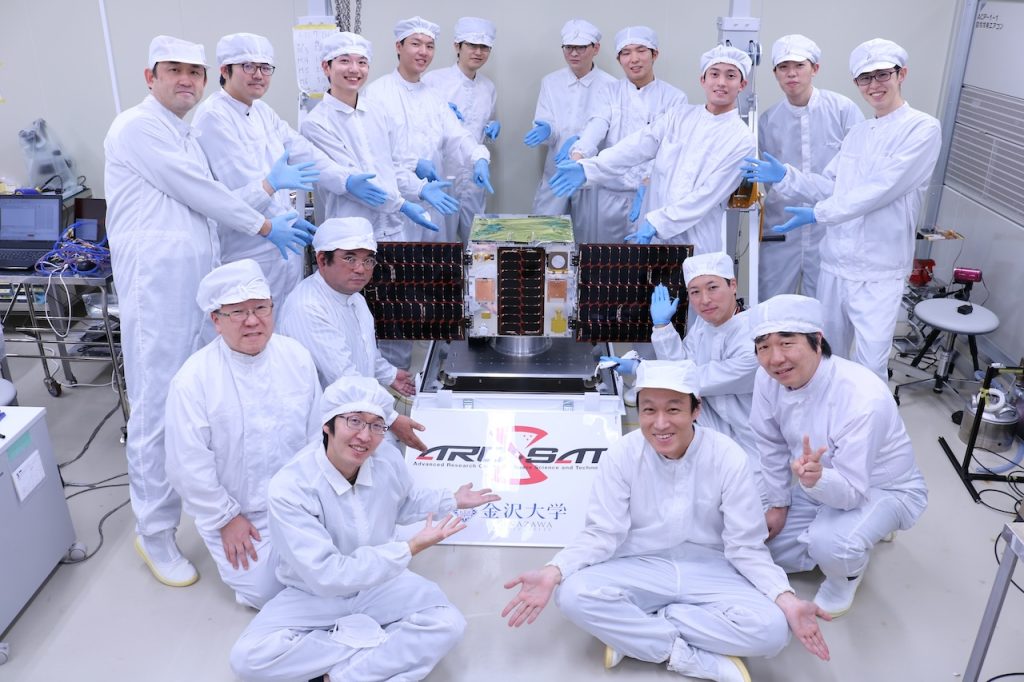

②Kanazawa University’s Second Satellite: “IMPACT”
IMPACT aims to investigate various plasma phenomena in space, such as those generating auroras, caused by electromagnetic waves. The mission seeks to understand how these waves propagate, interact with charged particles in Earth’s magnetosphere, and influence the space environment.
Key technologies on board include:
- AI Onboard Processor (AI-OBC): Intelligent processing of vast scientific data for rapid analysis.
- Miniature Electromagnetic Wave Sensor: High-precision detection of faint natural radio waves.
- Compact Extension Mechanism: Deployment device for electromagnetic wave sensors in space.
③Kanazawa University CubeSat Series: KSAT3-X
The KSAT3-X series is a microsatellite project focusing on innovation and talent development. This series revolves around three principles:
- eXperiment: Providing opportunities to test new technologies and ideas.
- eXperience: Offering students hands-on experience in all satellite development phases, from design to operation.
- eXpress: Accelerating development cycles to achieve results within 2.5 years.
What is a CubeSat ?
A CubeSat is a small cube-shaped satellite measuring 10 × 10 × 10 cm and weighing no more than 1.33 kg. Since the successful launch of the first CubeSat by the University of Tokyo and Tokyo Institute of Technology in 2003, it has become a popular platform for utilizing cutting-edge technologies in space due to its short development cycle.
Advantages of the KSAT3-X Series
- Student Development
Students gain hands-on experience in the full satellite development process, even within short academic programs. - Efficient Development
Standardized components and streamlined processes shorten development timelines. - Building on Experience
Leveraging the knowledge gained from KOYOH and IMPACT to integrate advanced space observation technologies and cultivate skilled professionals.